Probiotics And Celiac Disease
Probiotics and celiac disease. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of probiotics in improving gastrointestinal GI symptoms and quality of life QOL in patients with CD. This can take the form of increased permeability and changes in the gut microbiota. Many patients with celiac disease CD experience persistent symptoms despite adhering to the gluten-free diet.
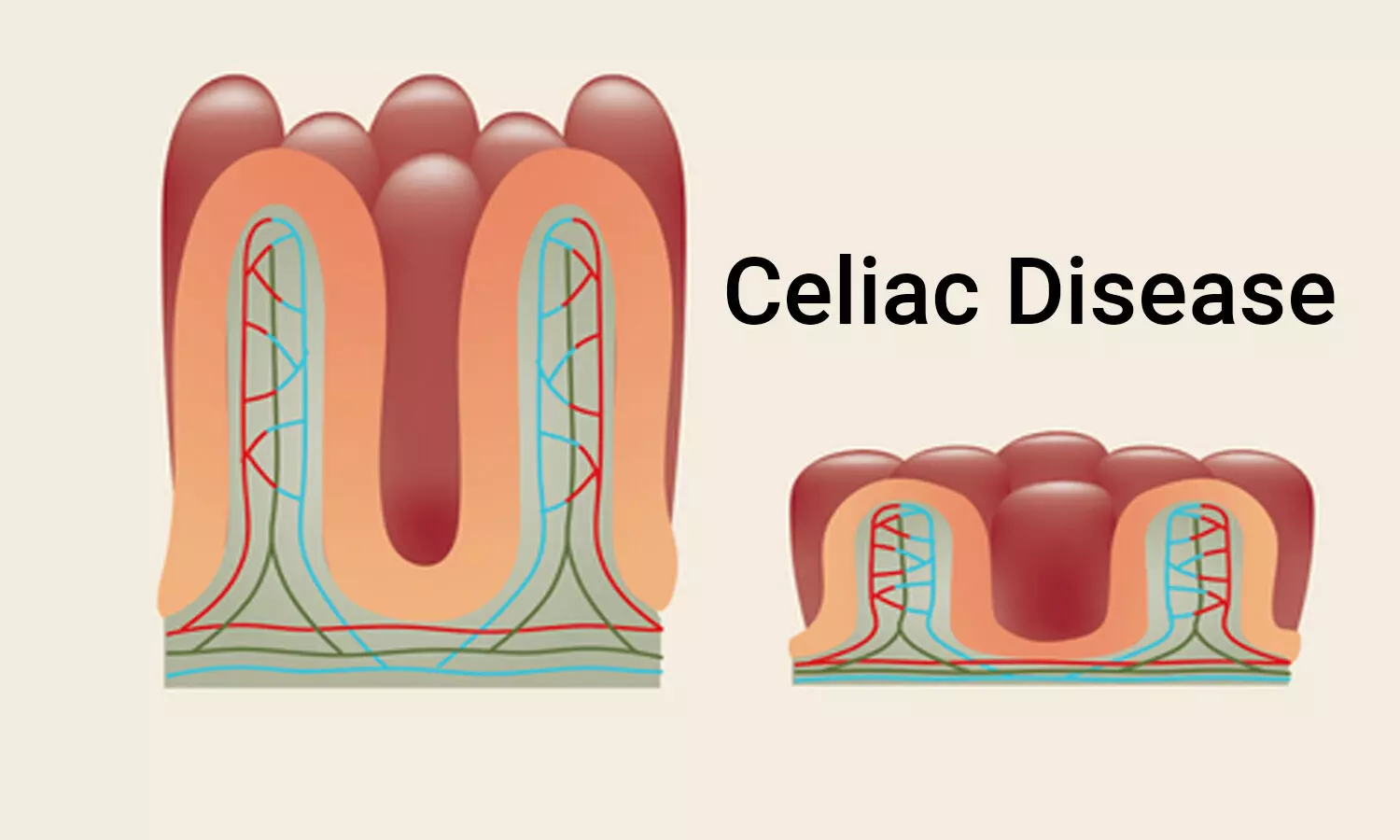
The damage caused to the lining of the small intestine is from a reaction of eating gluten a protein found in wheat rye and barley. Some probiotic strains found in this study to be effective against the toxic effects of gluten are Lactobacillus fermentum and Bifidobacterium lactis. For this reason probiotics are appearing as an interesting adjuvant in the dietetic.
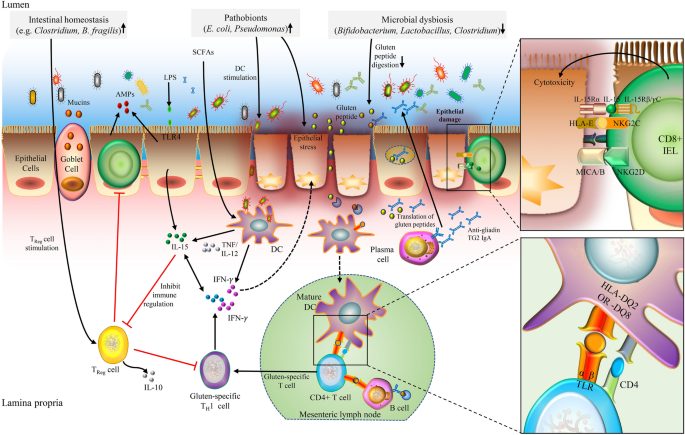
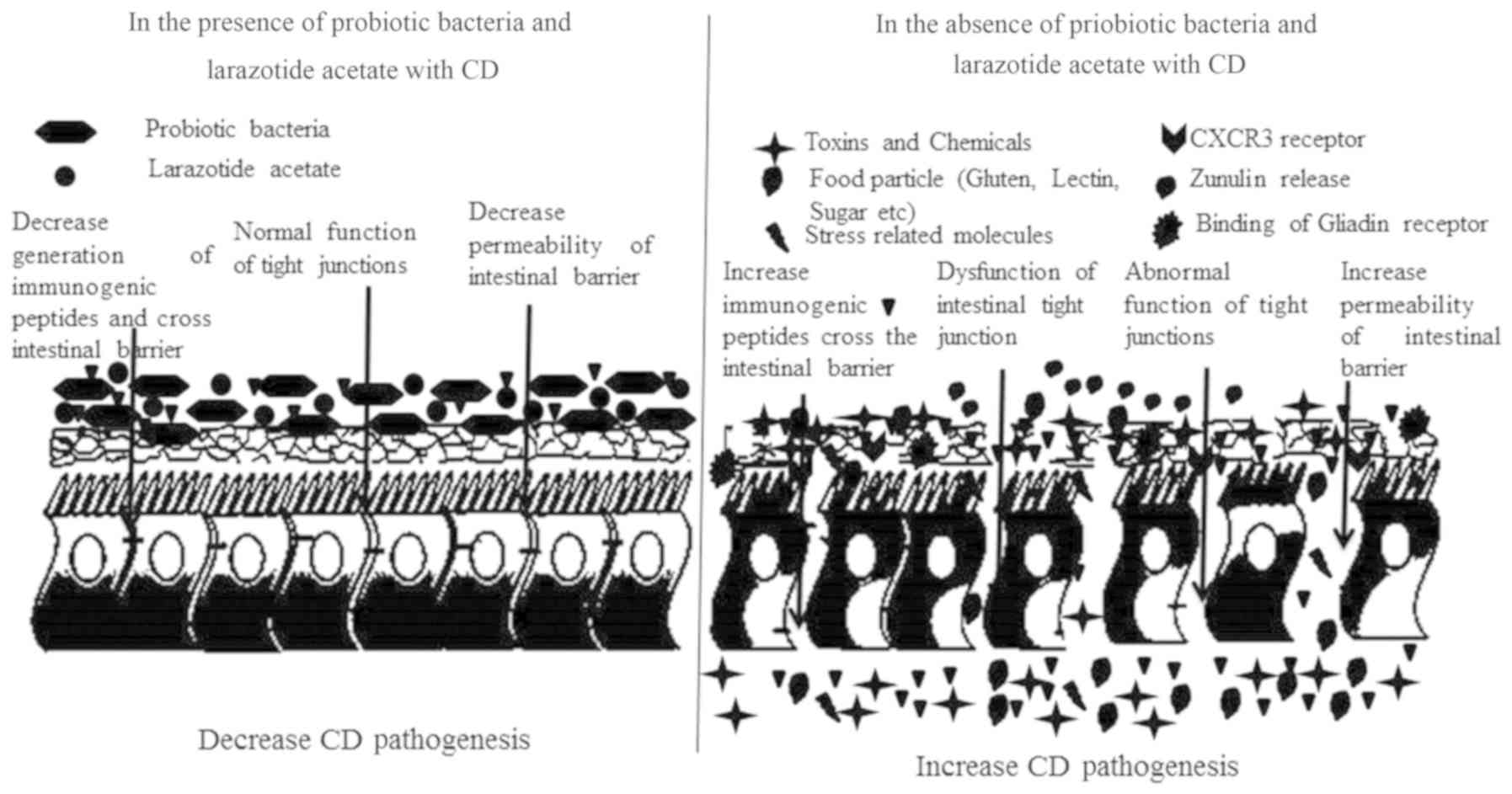
Celiac Disease Foundation has taken steps to address this situation demanding of both the FDA and the state attorney general more stringent regulations in labeling the contents of probiotics to ensure the consumer is not inadvertently consuming gluten. The good news is that preliminary studies found types of friendly bacteria in probiotics with the ability to degrade gluten. Laboratory studies suggest that probiotics may contribute to gastrointestinal health specifically in patients with celiac disease by fortifying the protective mucus layer that lines the gastrointestinal tract dampening the inflammatory response caused by gluten ingestion decreasing intestinal permeability the leakiness of the intestinal surface in response to gluten and possibly by aiding in gluten digestion.
The probiotic that pulverizes gluten New research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that a type of probiotic called Bifidobacteria could help people with celiac disease overcome residual symptoms and potentially act as a treatment for the disease in the future. For celiac disease patients exposure to gluten means intestinal damage. And past research has shown probiotics may help heal intestinal barrier function in people with celiac disease ii as well as alleviate the severity of the condition by influencing inflammation to varying degrees.
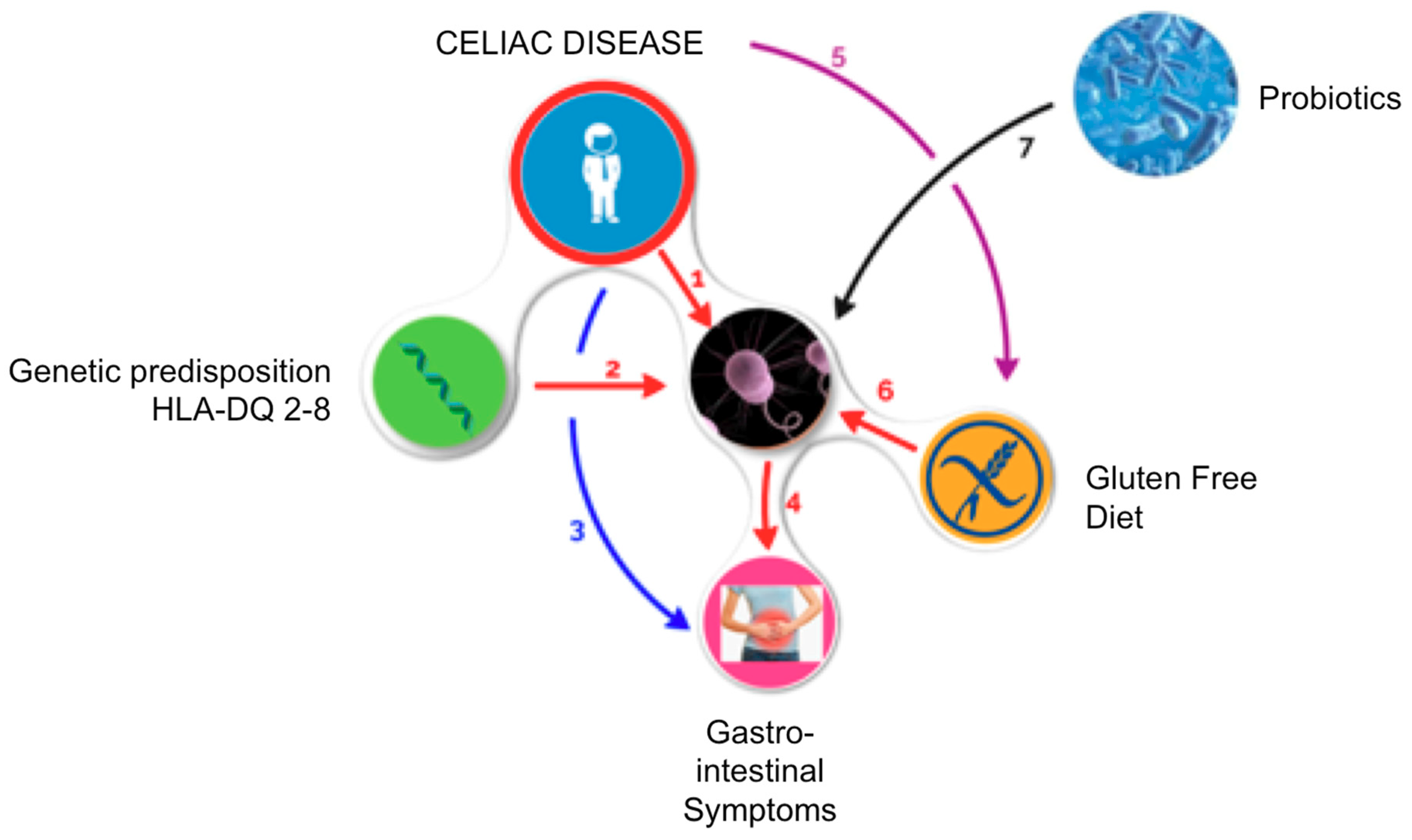
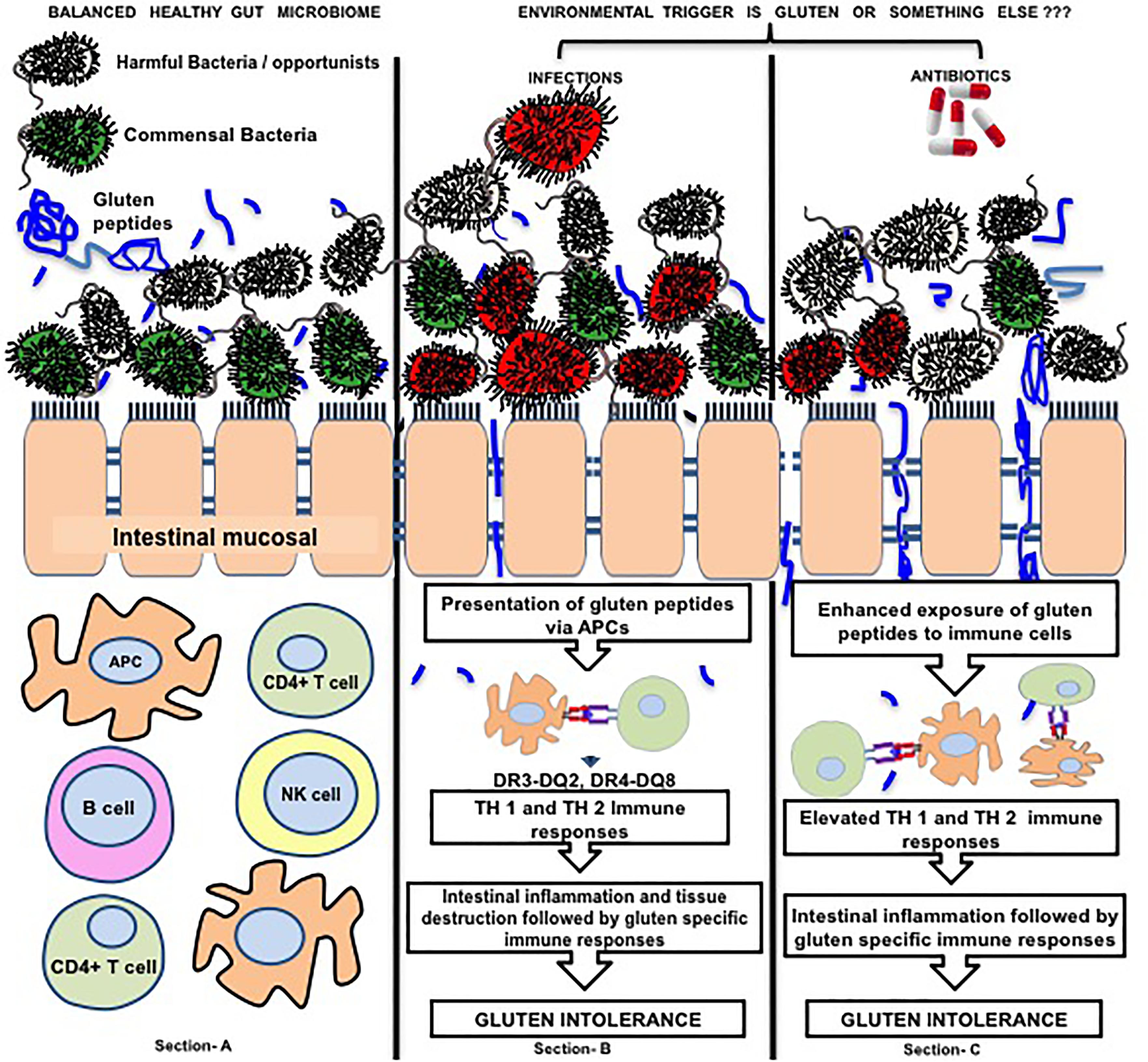
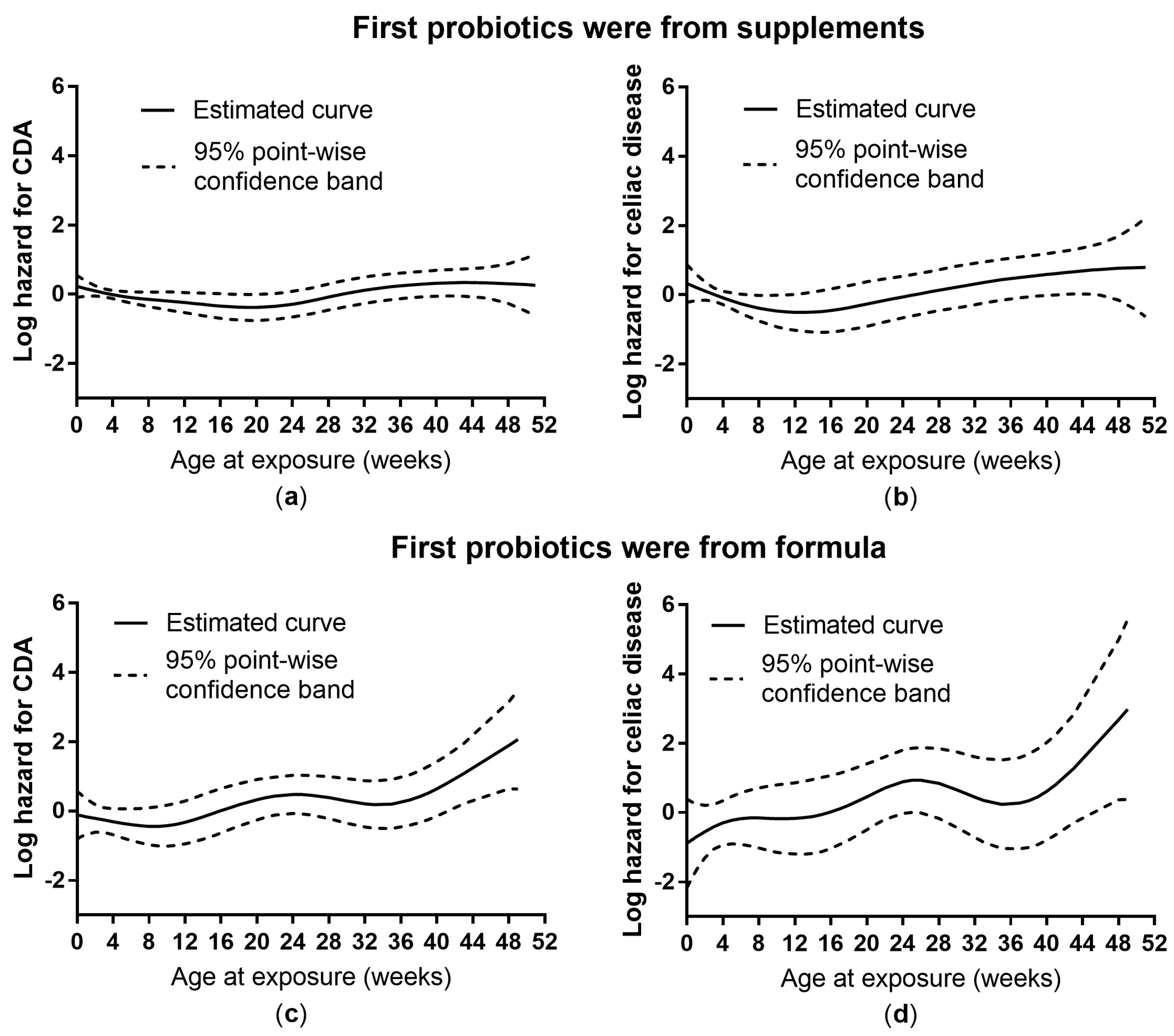
Studies show that probiotics can decrease inflammation when gluten exposure occurs. Different studies have assessed the use of probiotics as an adjuvant treatment for celiac disease. Celiac disease CD is an immune-mediated enteropathy correlated to the gluten ingestion in genetically predisposed subjects.
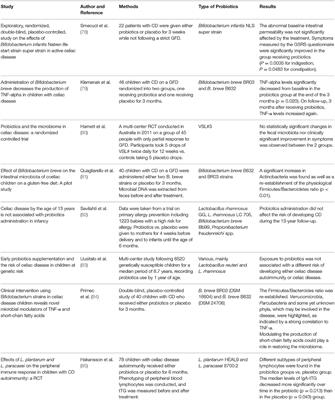
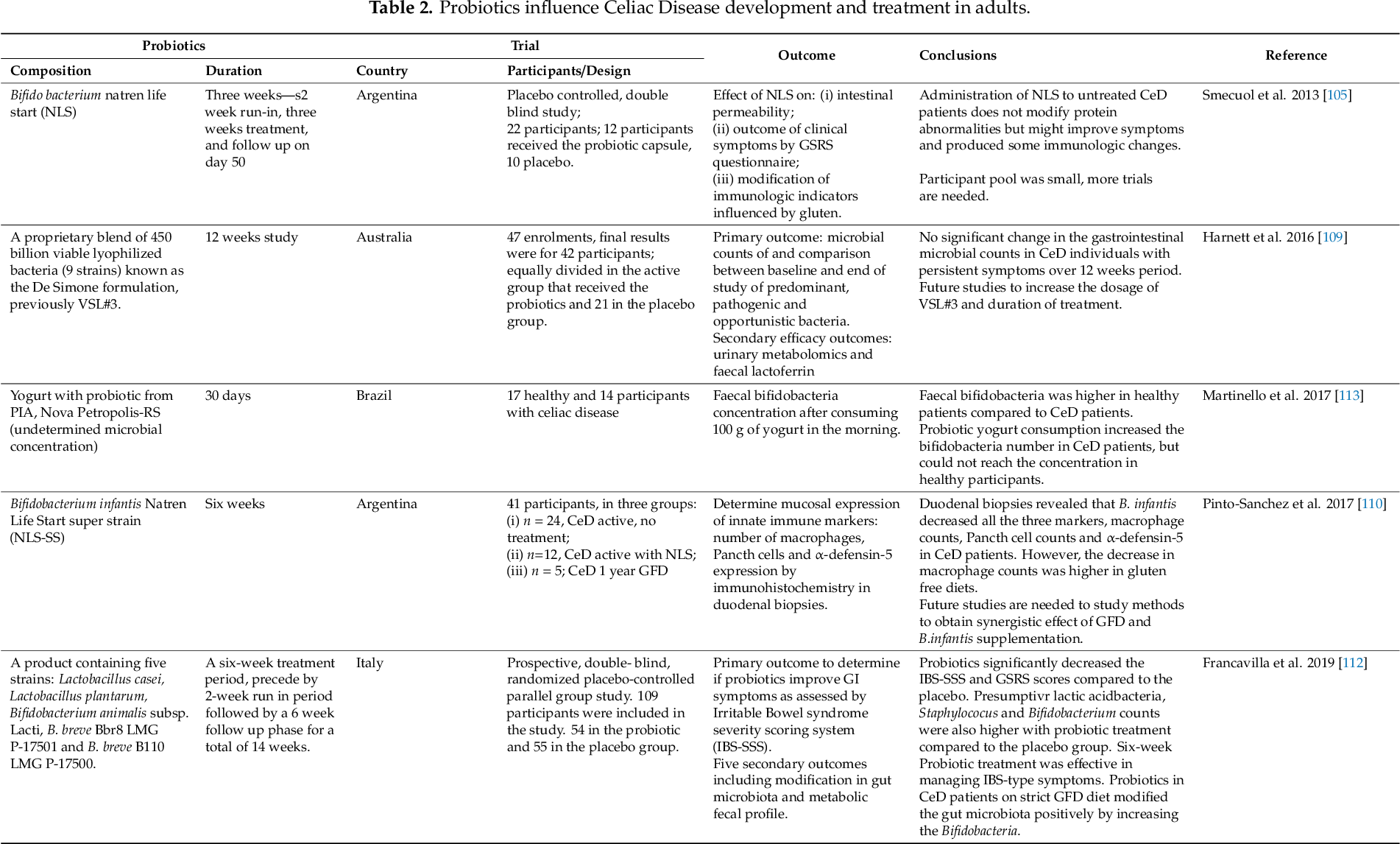
A few showed that probiotics might be beneficial in improving symptoms of celiac disease. To date the only therapy for CD is the complete exclusion of dietary sources of grains and any food containing gluten. Different studies have assessed the use of probiotics as an adjuvant treatment for CD.
Probiotics are widely regarded as beneficial for digestive health and may offer benefits for patients with celiac disease. However in the presence of microbial imbalance and particula.
And past research has shown probiotics may help heal intestinal barrier function in people with celiac disease ii as well as alleviate the severity of the condition by influencing inflammation to varying degrees.
Different studies have assessed the use of probiotics as an adjuvant treatment for celiac disease. The damage caused to the lining of the small intestine is from a reaction of eating gluten a protein found in wheat rye and barley. This is especially important in the long-run to CDFs patient-powered research network PPRN for celiac disease which will help patients. For this reason probiotics are appearing as an interesting adjuvant in the dietetic. Celiac disease is characterized by a sensitivity to gluten a protein that is found in grains like wheat rye and barley. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of probiotics in improving gastrointestinal GI symptoms and quality of life QOL in patients with CD. Iii It is also possible that the millions of people who suffer from out of intestine varieties of celiac disease or wheat intolerance which can express itself in over 125 health conditions iv may. Many people with celiac disease experience persistent symptoms despite adhering to the gluten-free diet. SUMMARY Celiac disease CD is a common chronic autoimmune enteropathy caused by gluten intake.
Some probiotic strains found in this study to be effective against the toxic effects of gluten are Lactobacillus fermentum and Bifidobacterium lactis. Laboratory studies suggest that probiotics may contribute to gastrointestinal health specifically in patients with celiac disease by fortifying the protective mucus layer that lines the gastrointestinal tract dampening the inflammatory response caused by gluten ingestion decreasing intestinal permeability the leakiness of the intestinal surface in response to gluten and possibly by aiding in gluten digestion. Different studies have assessed the use of probiotics as an adjuvant treatment for CD. Fasano et al VSL3 probiotic preparation has the capacity to hydrolyze gliadin polypeptides responsible for Celiac Sprue Biochimica et Biophysica ActaMolecular Basis of Disease vol. Different studies have assessed the use of probiotics as an adjuvant treatment for CD. Probiotics in Celiac Disease Recently the interest in the human microbiome and its interplay with the host has exploded and provided new insights on its role in conferring host protection and regulating host physiology including the correct development of immunity. The good news is that preliminary studies found types of friendly bacteria in probiotics with the ability to degrade gluten.




































Posting Komentar untuk "Probiotics And Celiac Disease"